 |
|
IN THIS ISSUE:
» Designing An Ultra-Thin Stepdown Converter: Multiphase Vs. Multilevel
» Inductorless Heater Switch-Mode Control Enhances Configurability Of Server Motherboards
» Novel 54-V to 12-V Buck Topology Eases Efficient Power Delivery In Data Centers
» Focus On Magnetics:
Understanding Core Magnetization In Current Transformers—Avoiding Saturation And Dangerous Output Voltage
» Spotlight On Safety & Compliance:
New EU Appliance Regulations Add Complexity, Reform Product Labeling
» New Power Products
» Industry Events:
- WiPDA Asia Explores Emerging SiC And GaN Technology
- PCIM Europe 2020 Goes Digital
» Other Top Power News
» In Memoriam...
From the Editor's Desk David G. Morrison
Editor, HOW2POWER TODAY

New twists on familiar power supply topologies and surprising new uses for less popular ones, together with wide-bandgap semiconductors and new power system architectures, are helping designers to solve power design challenges in consumer and data center applications. Examples of such topological inspirations are found in two of this month’s contributed features. First, we have Jianjing Wang’s article weighing the benefits of a multi-level converter versus a multiphase buck for implementing an ultra-thin 250-W power converter for a notebook application. While multilevel topologies are commonly seen at high voltage, this one, which leverages GaN’s advantages, operates at 48-V input. Meanwhile, Paolo Sandri’s article discusses his company’s Stacked Buck converter as it benefits the 48-V power architectures in data centers. This topology satisfies requirements for efficient generation of a regulated 12-V bus, yet is also scalable. While each article draws conclusions about a particular topology’s advantages in the targeted applications, the preliminary discussions highlight the fact that multiple topology options were considered—either by the author’s company or more broadly by the customers in the targeted market. I believe the implicit message is that power semiconductor developers will continue to explore new topology options because they have the tools to do so—new power switches, deep power circuit design experience and ever-expanding abilities to integrate—and because new power system architectures and new application requirements beckon. This issue of the newsletter also brings interesting discussions on other topics such as a power supply solution for embedded heaters used to rework processor ICs, an article discussing how to avoid core saturation and excessively high voltages in current transformers, EU energy efficiency regulations for appliances and more.
|
|

 |
 |

|
HOW2POWER EXCLUSIVE DESIGN ARTICLES 
|
Designing An Ultra-Thin Stepdown Converter: Multiphase Vs. Multilevel
by Jianjing Wang, Efficient Power Conversion, El Segundo, Calif.
This article examines the feasibility of adopting various nonisolated dc-dc stepdown topologies for an ultra-thin 48-V to 20-V, 250-W power solution. After some comparison of several topology options, two of these converter topologies, namely the two-phase buck and the three-level buck, were selected for comparison. Converters based on these topologies were then designed, built and tested. GaN FETs were used in these designs to further reduce the converter size and improve efficiency beyond what could be achieved using silicon MOSFETs. This article describes each design and evaluates the experimental results obtained in each case to determine which approach offers the optimal solution for this demanding application.
Read the article…
|
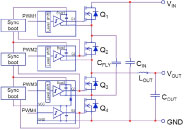
As the market continues to increase its
demand for thinner power supply
solutions with greater power density,
new approaches such as multi-level
converters merit consideration. |

|
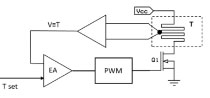
Control of the heater temperature is
facilitated by control of the current
through the heater trace using a
switching voltage regulator capable
of providing current control over a
wide range. |
Inductorless Heater Switch-Mode Control Enhances Configurability Of Server Motherboards
by Viktor Vogman, Power Conversion Consulting, Olympia, Wash.
The increase in server complexity has resulted in a growing need for better and easier motherboard (MB) configurability. To meet this requirement, server MB developers recently unveiled a new technology that facilitates MB reconfiguration with a so-called rework grid array (RGA) interposer. Such an interposer is composed of a ball grid array or an IC package support structure, which has electric heaters embedded in its foundation layer. The heaters supply heat locally to reflow solder and thereby enable attachment or detachment of the IC or the processor package. This RGA-based reconfiguration method provides cost advantages over sockets or desoldering/resoldering equipment. The power required to activate the RGA heater can be supplied from the MB power supply, e.g. a 12-V bus. This article studies the electrical design of the RGA heater control to make this circuitry highly efficient, as well as cost- and size-optimized.
Read the article…
|

Novel 54-V to 12-V Buck Topology Eases Efficient Power Delivery In Data Centers
by Paolo Sandri, STMicroelectronics, Santa Clara, Calif.
Power consumption from hyperscale data centers poses numerous challenges to the design community to deliver power more efficiently to meet continuously growing demand. One key means to address this challenge is to move the rack bus bar power distribution from the traditional 12 V to 48 V (54 V nom.) as this offers lower distribution losses. Changing the dc input bus requires developing new topologies to efficiently manage the conversion from the 54-V/48-V bus and “smoothly merge” with the current 12-V ecosystem in the least invasive way while delivering the best overall power efficiency gain. This article presents the details of the newly developed ST Stacked Buck topology (STB), which delivers a high-efficiency, high-density, regulated 12-V bus.
Read the article…
|
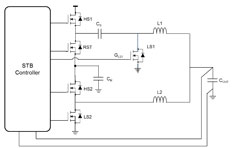
An STB cell consists of a two-phase
buck where the phases are connected
in series on the input side and
paralleled on the output side. |


FOCUS ON MAGNETICS 
Sponsored by Payton Planar Magnetics
A monthly column presenting information on power magnetics design, products, or related technology |

Understanding Core Magnetization In Current Transformers—Avoiding Saturation And Dangerous Output Voltage
by Gregory Mirsky, Vitesco Technologies, A Spinoff Of Continental Automotive Systems, Deer Park, Ill.
Current transformers (CTs) are used as ac current sensors and power handling devices in current-fed power supplies. Very often CTs operate in circuits where the primary current has a dc component. This dc magnetization adds more magnetic flux to the core, leaving less headroom for the ac magnetizing. Therefore the CT design or selection should be based on the maximum or peak operating flux density of the core. It is also important to note that the CT is supplied from a very high impedance current source and has just one turn (usually) on the primary winding. This makes the primary turn(s) a magnetizing winding. Meanwhile, the output is a parallel connection of the secondary winding and load. This creates very high voltage at no load and zero secondary volts with a load short. Therefore no-load operation may pose a danger to an operator or destroy equipment if the load resistor does not have a low enough value.
Read the full article…
|
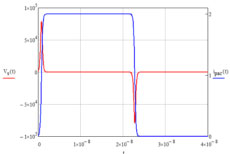
The secondary voltage on a CT
can go up to very high values,
which may only be limited by the
core saturation or internal or
external voltage breakdown. |

 |
 |

SPOTLIGHT ON SAFETY & COMPLIANCE 
Sponsored by Power Integrations
A monthly column discussing standards and regulatory requirements affecting power electronics |

New EU Appliance Regulations Add Complexity, Reform Product Labeling
by Kevin Parmenter, Chair, and James Spangler, Co-chair, PSMA Safety and Compliance Committee
In Europe there are newer, updated regulations for energy efficiency targeting consumer white goods which we could see adopted as best practices globally. The new regulations also include changes in the labeling for appliances. The main purpose of these labeling changes is to allow the consumers to make better purchasing decisions. Ultimately, the goal of these changes in energy efficiency and labeling requirements is to achieve energy efficiency objectives for the region. Besides modifying efficiency requirements, the new EU regulations also impose limits on audible noise since many appliances contain motors. These changes in EU appliance regulations are the subject of an upcoming webinar by Power Integrations on “EU Ecodesign and Energy Labeling Directives,” which will be presented by David Chen. This article highlights some of the key regulatory changes to be discussed in this webinar.
Read the full article…
|

 |
 |

 — POWER PRODUCTS IN 3 IMAGES OR LESS — POWER PRODUCTS IN 3 IMAGES OR LESS 
|
INDUSTRY EVENTS  |
|
WiPDA Asia Explores Emerging SiC And GaN Technology
The IEEE Workshop on Wide Bandgap Power Devices and Applications in Asia (WiPDA Asia 2020) which will be held this year September 23-25 in Kyoto, Japan, focuses on emerging technology in power electronics related to wide-bandgap power semiconductor devices. In particular, it focuses on SiC and GaN power devices which have experienced significant progress recently. Among the highlights of this event, Professor Matsunami, who is a leading authority on SiC semiconductor materials and devices, will present a detailed history of SiC semiconductor material and power device development.
Read the full story…
|

|
|
PCIM Europe 2020 Goes Digital
Due to the increasing spread of COVID-19 in Europe and the associated ban on all major German events up to, and including the end of August, the PCIM Europe exhibition and conference 2020 in Nuremberg has been cancelled. The event will now be scheduled to take place as a live event next year. But in the meantime, a virtual format known as “PCIM Europe digital days” will be held July 7-8, 2020.
Read the full story…
|
OTHER TOP POWER NEWS
|
|
 The IEEE Long Island Power Electronics Symposium, which is scheduled for November 5, 2020 in Hauppauge, NY is seeking 45-minute lectures covering applicable topics including but not limited to power conversion tutorials, novel design concepts in power conversion, energy storage, power management, power integrity and emerging trends. For more information, see the call for papers. The IEEE Long Island Power Electronics Symposium, which is scheduled for November 5, 2020 in Hauppauge, NY is seeking 45-minute lectures covering applicable topics including but not limited to power conversion tutorials, novel design concepts in power conversion, energy storage, power management, power integrity and emerging trends. For more information, see the call for papers.



 Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the IEEE Nuclear and Space Radiation Effects Conference (NSREC 2020), which was originally to be held in July, has been rescheduled to December 1-4, 2020. The Hilton Buffalo Thunder in Santa Fe, New Mexico remains the venue. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the IEEE Nuclear and Space Radiation Effects Conference (NSREC 2020), which was originally to be held in July, has been rescheduled to December 1-4, 2020. The Hilton Buffalo Thunder in Santa Fe, New Mexico remains the venue.
 The dates for PCIM Asia 2020 have been moved to November 16-18 due in part to disruptions to international travel resulting from COVID-19 pandemic. The dates for PCIM Asia 2020 have been moved to November 16-18 due in part to disruptions to international travel resulting from COVID-19 pandemic.

IN MEMORIAM...  |
|
Professor Thomas A. Lipo, a legendary figure in the field of electrical machines, power electronics, and drives, passed away on May 8. Prof. Lipo was a co-founder of WEMPEC, the Wisconsin Electric Machines and Power Electronics Consortium at UW-Madison. For more information and to post tributes or messages of sympathy, see Bulent Sarlioglu’s LinkedIn post, and the online obituary.
|

ABOUT THIS NEWSLETTER: Thank you for reading HOW2POWER TODAY.
How2Power sends no more than one e-mail per month to registered users. Continuing your subscription ensures you'll receive future newsletters. Manage Your Subscription
©2020 All rights reserved. www.how2power.com
|
|
|